
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website.
By using this site, you agree to our use of cookies. Find out more.
Business processes are key to how organizations function internally and serve customers. However, many business processes involve repetitive manual tasks that can slow down operations and reduce productivity
Business processes are key to how organizations function internally and serve customers. However, many business processes involve repetitive manual tasks that can slow down operations and reduce productivity. With advances in technology, more and more processes are being automated using various techniques. This blog discusses the different types of Business Process Automation that are available for organizations to streamline their operations. Understanding the distinctions between task automation, workflow automation, process automation, robotic process automation, and intelligent automation is important for companies looking to leverage the right technologies.
Here are some specific types of business process automation:
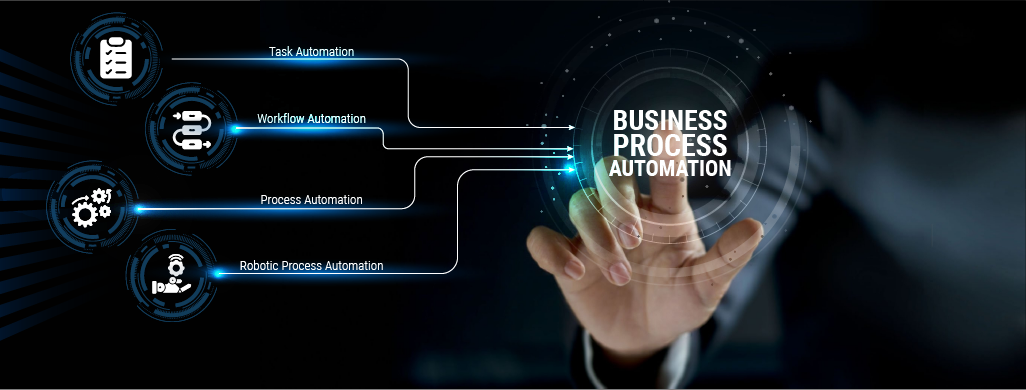
Task automation refers to automating individual tasks or activities within a business process. These are typically repetitive tasks that take up employees' time but require minimal judgment. Common examples include data entry, routine form filling, invoice processing, and document formatting. Task automation leverages technologies like macros, scripts, and simple rule-based algorithms to complete standard tasks without human involvement. This allows tasks to be completed considerably faster with fewer errors compared to manual processes.
Task automation is often one of the first steps organizations take when beginning their automation journey. Simple repetitive tasks can quickly be identified and automated with minimal effort through technologies immediately available to most companies. This delivers faster results from automation while requiring less upfront investment and planning compared to larger process automation initiatives. Task automation also allows companies to ease into more advanced types of automation by automating discrete tasks before linking them together into broader workflows and processes.
Workflow automation involves linking individual tasks together into a defined sequence or workflow. It coordinates the flow of work across different tasks and ensures tasks are completed in the correct order with the right dependencies and hand-offs in place. Workflow automation builds on task automation by stringing discrete steps together into an end-to-end process flow. Technologies like workflow management systems, robotic workflow automation tools, and business process management systems are commonly used for workflow automation.
Workflow automation helps improve efficiency by enforcing process standardization and reducing errors from manual hand-offs between steps. It allows workflows to be triggered automatically based on pre-defined rules and conditions. For example, the approval of an invoice can automatically trigger its payment processing and accounting. This makes processes more consistent and ensures time-consuming tasks remain on track. Workflow automation is more complex to implement than discrete task automation but delivers higher productivity gains by integrating multiple automated tasks into one repeatable workflow.
Process automation involves automating an entire business process from end to end without any manual handovers between steps. It aims to fully automate processes that may involve multiple workflows, activities and decisions. Process automation subsumes both task and workflow automation by incorporating automated tasks, their dependencies and overall process logic. Technologies like process mining, process modelling and business process management systems are commonly leveraged for process automation.
Process automation allows organizations to completely remove human involvement from repeatable processes. For example, the full order to cash process involving order placement, delivery tracking, billing and payment collection can be automated. This results in the most efficient and highest scale of automation since complete processes are digitized. While complex to achieve, process automation delivers substantial benefits through uniform process execution, centralized performance monitoring and data capture across all process steps. It frees up employees to focus on more strategic work by taking over routine processes in their entirety.
Robotic process automation involves configuring software robots or virtual bots to emulate human actions and decision-making to complete repetitive tasks across various systems. RPA bots are able to retrieve data from one system, populate it into another system by interpreting screenshots, web forms and databases just like humans do. RPA is commonly used to automate routine back-office tasks like data entry, invoice processing, form filling, report generation etc. It utilizes rule-based decision capabilities of software robots for tasks that require guidelines but not complex judgement.
RPA provides a powerful yet easy way for organizations to quickly automate rule-based human jobs and processes. It does not require heavy coding or technical integration with existing IT systems. RPA bots can be easily configured using a graphical user interface which makes automation accessible even to non-technical teams. RPA has become very popular in recent years due to its swift implementation capabilities and rapid return on investment from replacement of manual FTE roles with digital robots. It serves as a crucial first step towards more advanced types of process and workflow automation.
Robotic process automation is evolving rapidly with new technological advancements. As RPA becomes more sophisticated, advanced capabilities are emerging that will reshape automation strategies for manufacturers.
Task automation, workflow automation, Business Process Automation, robotic process automation, and intelligent automation are all important approaches for automating business functions. The degree of human involvement, technical complexity, upfront investment needs, and resulting benefits vary across these methods. Organizations should evaluate their process needs, automation objectives, and technical capabilities to decide the most suitable automation strategies. A combination of RPA for task automation followed by intelligent automation for complex workflows is a common path that delivers steady productivity gains. Process automation should be the long-term goal to fully optimize key business processes. The right blend of these automation types can significantly boost efficiencies, cut costs and free up resources for strategic work.
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published.